Jake Miller: 2024 Technology Predictions
1. Evolving Human-Computer Interactions & Interactive AI
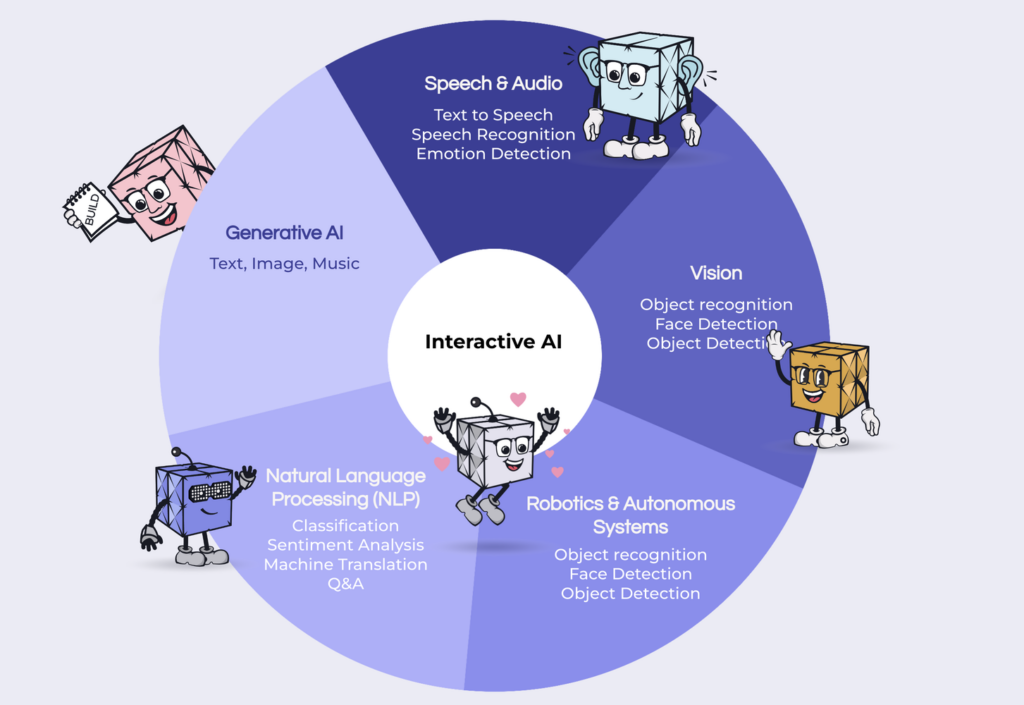
How humans interact with computers will gradually shift in 2024. This change will involve increased comfort with digital humans, leading to more personal interactions with AI entities. At The Engineered Innovation Group (EIG), we are already working on several projects that combine natural language processing (NLP), vision, speech and audio, and generative AI technologies. We’ll announce more soon, but suffice to say this is a new frontier in human-computer interaction (HCI).
Leaders in the industry are also driving this domain forward. One of them, Google DeepMind co-founder Mustafa Suleyman, believes that the future of AI assistants will be in their ability to interact with humans in an advanced manner.
“The third wave will be the interactive phase,” Suleyman told MIT Technology Review in September. “That’s why I’ve bet for a long time that conversation is the future interface. You know, instead of just clicking on buttons and typing, you’re going to talk to your AI.”
How we type in commands and interact with computers via mouse and keyboard will be slowly displaced, and the trend will start this year. I am bullish on being a leader in this space, too.
The landscape of HCI is poised to undergo a transformative shift, moving beyond the traditional mouse and keyboard paradigm. Human-voice interaction is a key player in this evolution, rapidly advancing thanks to improvements in natural language processing and machine learning. This technology enables users to control computers using voice commands. It is also progressing towards a future where individuals can verbally instruct computers to write and integrate their own code, dramatically simplifying the software development process.
Alongside voice interaction, technologies like Apple’s VisionPro and Microsoft’s HoloLens are pioneering new frontiers. Apple’s VisionPro, an advanced iteration of augmented reality (AR) technology, could offer intuitive, gesture-based interactions, seamlessly blending digital information with the physical world. Similarly, Microsoft’s HoloLens, an already established mixed reality platform, continues to evolve, offering immersive experiences that combine elements of both the digital and physical worlds.
These AR and mixed reality technologies not only revolutionize gaming and entertainment but also have profound implications for fields like education, engineering, and medicine, where they can provide interactive, three-dimensional visualizations and hands-on experiences without the constraints of traditional screens. As these technologies mature, they promise to redefine how we interact with computers, making these interactions more natural, intuitive, and aligned with human behaviors and environments.
2. Edge Computing’s Growing Importance
In 2024, edge computing will become increasingly vital for rapid data processing. This technology, which involves processing data closer to where it’s generated rather than in a centralized data-processing warehouse, is set to become as essential as traditional central computing. Sources like Gartner have highlighted the growing edge computing trend in recent years.
Gartner predicts that by 2026, 15% of on-premises production workloads will run in containers, up from less than 5% in 2022. This shift necessitates new types of infrastructure, including edge infrastructure for data-intensive use cases. Edge computing is essential for handling modern applications’ increasing data processing demands, especially those requiring real-time analytics and decision-making.
The trend towards adopting cloud principles in on-premises data centers is also driving the growth of edge computing. Gartner estimates that by 2027, 35% of data center infrastructure will be managed from a cloud-based control plane, up from less than 10% in 2022. This shift indicates a move towards more distributed computing models, where edge computing plays a crucial role.
The growth of the IoT market, estimated to reach $1.4 trillion by 2027, is closely linked with the adoption of edge computing. As more devices connect and generate data, processing this data closer to the source becomes increasingly important. Edge computing allows for more efficient data collection and processing, reducing latency and bandwidth use.
3. Healthcare without Walls
The concept of “Healthcare Without Walls” is gaining traction and is expected to be a significant trend in 2024. This approach to healthcare delivery focuses on extending medical services beyond traditional hospital settings, leveraging technology and innovative practices to reach patients wherever they are. The trend is driven by the increasing adoption of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring technologies, which have shown effectiveness during the COVID-19 pandemic.
One of the key factors propelling this trend is the continued support and flexibility from healthcare regulators and payers. For instance, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) have implemented waivers and flexibilities that allow healthcare providers to offer a broader range of services remotely. These changes, initially a response to the pandemic, are evolving into more permanent healthcare delivery models. The expansion of telehealth services, including the ability for healthcare providers to offer care across state lines and the reimbursement for telehealth visits, is a critical component of this trend. Additionally, remote patient monitoring tools are becoming more prevalent, enabling healthcare providers to manage chronic conditions and provide continuous care without the need for physical office visits.
In 2024, “Healthcare Without Walls” is expected to continue growing, driven by technological advancements, changing patient expectations, and an increasing focus on cost-effective and accessible healthcare solutions. This trend represents a shift towards a more patient-centric healthcare system, where convenience, accessibility, and personalized care are paramount. As technology continues to evolve, it will play a crucial role in enabling this transition, offering new ways to deliver care and manage patient health remotely.
4. Rise of Healthcare Connected Devices
In 2024, the use of connected devices in healthcare is expected to increase. These devices, ranging from wearable health monitors to remote patient monitoring tools, are becoming crucial in managing chronic diseases and enhancing patient care.
The use of connected devices in healthcare is indeed expected to increase significantly. This trend is driven by the growing adoption of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies across various sectors, including healthcare. According to a forecast by Transforma Insights and Exploding Topics, the number of IoT devices worldwide is projected to almost double from 15.1 billion in 2020 to more than 29 billion by 2030. In the healthcare sector, this increase is manifested in the rising use of wearable health monitors and remote patient monitoring tools, which are becoming increasingly crucial for managing chronic diseases and enhancing patient care.
Wearable fitness technology, for example, has become a significant part of the healthcare industry. Devices such as FitBits and smartwatches are now mainstream, with their use more than tripling in the last four years. The demand for these wearables is expected to continue rising as consumers show increased interest in monitoring their health and vital signs. The US smart wearable user market is projected to grow by 25.5% year-over-year in 2023, up from 23.3% in 2021, according to an October 2021 forecast by Insider Intelligence.
More than a quarter of the US population will use wearable devices in 2023. These devices are not only limited to fitness trackers but also include advanced health monitoring tools like wearable ECG and blood pressure monitors. The advancement of wearable technology and the growing demand from consumers to take control of their own health have influenced the medical industry, including insurers, providers, and technology companies, to develop more sophisticated wearable devices.
5. Accelerated Breakthroughs in Biology and Pharmaceuticals
Fields like biology and pharmaceuticals are poised for faster breakthroughs in 2024. This acceleration can be attributed to advancements in AI-driven biotechnology and drug discovery and increased investment in research and development.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) integration in pharmaceutical development and drug discovery is poised to continue its significant impact into 2024. Building on the momentum gained in 2023, AI and Machine Learning (ML) applications in the pharmaceutical sector are expected to revolutionize the industry further. The focus on ML for processing large volumes of molecular, biochemical, and genomic data is laying a solid foundation for innovative drug development approaches in 2024.
Key trends for 2024 include the expansion of synthetic data in drug research, particularly for overcoming barriers in accessing real-world data from patients’ electronic health records. This approach is crucial for anonymizing patient information while exploring a wider array of both structured and unstructured data variables, thereby advancing drug research. Additionally, pharmaceutical companies are predicted to forge more partnerships with virtual care providers, leveraging AI to educate providers on new drugs and ensure convenient patient access to prescriptions through online consultations.
Furthermore, AI-driven initiatives are transforming drug development processes, with data analytics and AI enabling researchers to gain deeper insights into disease mechanisms. This data-driven approach is expected to expedite the drug development process, leading to more effective therapies and improved patient outcomes. The use of Natural Language Processing (NLP) technology will continue to support regulatory compliance, helping pharmaceutical companies navigate the frequently changing nature of regulatory guidelines and data.
In summary, 2024 is set to witness an increased reliance on AI and ML in the pharmaceutical industry, from enhancing drug discovery to optimizing clinical trials, thereby accelerating the journey from laboratory research to patient care.
6. AI-Driven Solution Development – Developer-less Software Development
The rise of AI-generated integration is anticipated in 2024 when AI-driven solutions are developed directly for business users. This trend could reduce the need for traditional developers and intermediaries, streamlining the solution development process.
While there is significant advancement in AI technologies, especially in software development, AI replacing software developers in a manner akin to the conversational, integrative capabilities seen in Star Trek computers is still largely in theoretical or emerging technology. But, companies will begin pioneering this front.
AI technologies, particularly large language models (LLMs) like GPT-3 and GPT-4, are increasingly impacting software development. These models can assist in writing code, suggesting improvements, and increasing productivity. Generative AI tools are being integrated into the programming process, offering significant benefits in generating code prototypes, assisting with documentation, and providing insights into software architecture. These tools are reshaping how developers approach coding, making it more efficient and less focused on repetitive tasks.
7. Software Companies Embracing Services
In 2024, more software companies are expected to include a service component. The need for personalized solutions and ongoing customer support drives this shift towards service-oriented business models. Companies that can provide superior, faster, and cheaper solutions by leveraging generative AI will win.
8. Boost for VC-Backed SaaS Startups – But Only Some
Venture Capital (VC) backed Software as a Service (SaaS) startups will likely experience a surge in 2024. However, big investments will likely be made in companies that intend to put software companies out of business. (Read this = AI replaces the need for many SaaS point solutions).
The venture capital market in the US is expected to experience a mix of challenges and opportunities. There is an anticipation of an increase in “down rounds,” where valuations decrease across financings, primarily due to high-interest rates and other macroeconomic factors. However, artificial intelligence (AI) continues to be a major catalyst in the market, supporting new investments and fund commitments. Despite a less enthusiastic market for technology startups, ample capital is available for transactions in 2024, suggesting that strong companies will have good prospects.
The volume of private investment secondaries is projected to reach a new record level in 2024. Factors contributing to this growth include a substantial amount of dry powder, expected narrowing of the bid-ask spread, and ongoing market innovation. This optimism is driven by the substantial amount of capital available for new investments and the evolving strategies of secondary buyers.
AI startups are at the forefront of VC funding, with their ability to harness data, automation, and machine learning to solve complex problems across various industries. The excitement around AI, fueled by significant deals and advancements in generative AI, is expected to continue driving venture capital interest in 2024.
After a challenging 2023, there are signs of a rebound in VC fundraising. However, this rebound is not expected to reach the highs of 2020 and 2021. The market slowdown has led to a more selective and thoughtful approach to investment decisions, focusing on deal quality over quantity.
9. Higher Ed Troubles
The education system, particularly higher education, will face challenges in 2024. Universities emphasizing traditional academics over applied skills may need help attracting new students. This trend is evident in the declining university enrollment rates in the U.S., as practical skills gain more value in the job market.
AI is being used for personalized learning, where algorithms analyze students’ learning patterns and tailor the educational content accordingly. AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants are also being used for student support services, providing 24/7 assistance and enhancing student engagement. Adaptive learning technologies adjust the pace and complexity of learning materials based on individual student performance, ensuring that students receive support and challenges tailored to their specific needs.
VR and AR are revolutionizing fields like medicine, engineering, and architecture by providing immersive, interactive experiences that enhance practical learning and skill development. For example, medical students can practice surgeries in a virtual environment before performing real-life operations.
The advent of widespread access to online information and courses has initiated a paradigm shift in how we perceive and value educational achievements, moving beyond the traditional framework of institution-based diplomas. This digital revolution in education democratizes learning, making a vast array of knowledge and skill-building opportunities accessible to a global audience.
Online learning platforms often offer the flexibility to tailor education paths according to individual interests and career goals. This self-directed learning approach can be more engaging and relevant to learners, as they can focus on what they find most valuable for their personal and professional development.
Increasingly, employers are recognizing the value of online courses and micro-credentials. Especially in skill-centric industries, the focus is shifting towards what an individual can do and has demonstrably achieved rather than solely where they studied or what degree they hold.
10. Divergent AI Governance in Europe and the U.S.
AI governance and legislation are predicted to have contrasting effects in Europe and the U.S. in 2024. While European regulations might stifle innovation due to stringent controls, the U.S. is expected to foster AI innovation through supportive legislation. This prediction aligns with the current regulatory landscapes in these regions.
For example, the EU’s AI Act has outlawed emotion detection in business and education. Still, draft regulations by the California Consumer Privacy Act’ DRAFT AUTOMATED DECISIONMAKING TECHNOLOGY REGULATIONS do not restrict such use but do require the ability for users to opt out of various features that AI products may offer.
There’s a strong belief in letting innovation proceed with minimal government intervention, assuming that the market will find the best solutions. On the other hand, the EU tends to take a more precautionary approach, prioritizing the protection of its citizens’ rights and data privacy even if it means imposing stricter regulations on businesses.
American culture traditionally emphasizes individualism and entrepreneurship, which can translate into a greater willingness to trade off some degree of privacy for the perceived benefits of technology. In contrast, the EU highly values privacy and data protection, as evidenced by comprehensive regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
With its basis in common law, the U.S. legal system can be more reactive, developing regulations in response to emerging issues. The EU’s legal system, particularly in the context of the European Commission, is often more proactive in anticipating and regulating issues before they become widespread, as seen in their early adoption of comprehensive data protection and privacy laws.
There might be differences in public perception and trust in technology and AI between the U.S. and EU populations. If the public in the U.S. is generally more trusting or optimistic about the benefits of AI, there may be less push for stringent regulations.